December 3, 2022
之前写了个 C++ 的软件渲染器(详见:手写一个C++软件渲染器),其中的 Shader 部分是将 Shader 逻辑用 C++ 实现,然后静态编译进去的,没法直接执行真正的 Shader 代码(如 GLSL/HLSL 等),因此萌生了写个 Shader 虚拟机的想法,正好 Khronos 推出的 SPIR-V 意在统一 Shader 生态,因此写个 SPIR-V 的虚拟机更合适,于是便有了 SPVM 这个项目:
https://github.com/keith2018/spvm
首先看下 Khronos 官方对 SPIR-V 生态的描述
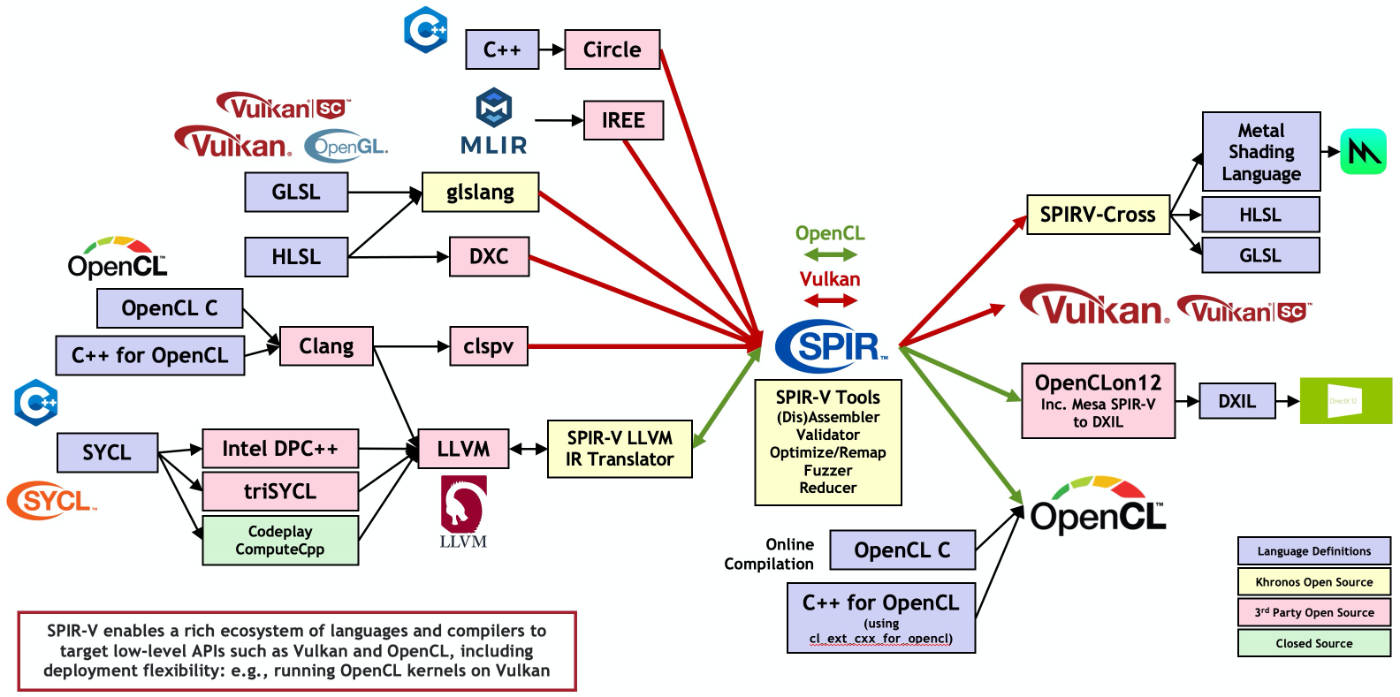
即目前不同的 Shader 语言代码(如 GLSL/HLSL/MSL 等)可以通过工具编译成 SPIR-V 字节码,然后又可以编译回不同的 Shader 语言代码,对于跨平台开发确实是好事,不过目前用的多的估计主要还是 Vulkan。
SPVM 目前只有解释执行模式,基本的用法流程:
- 将 Shader 代码(如 GLSL)用工具(如 glslangValidator )编译成 SPIR-V 二进制文件
- 使用 SPVM 加载 SPIR-V 二进制文件
- 设置好输入输出,如顶点、uniform 等
- 通过 SPVM 执行 Shader 的 main 函数,得到输出
SPVM 目前参考的标准主要有:
目前的一些限制:
- 部分指令不支持(GLSL 相关绝大部分都已支持),详细可查看指令支持列表:
- 只支持 32 位数值类型 (float, integer)
- 只支持 Addressing Model 为
Logical - 不支持 OpenCL 相关的指令
- 微分相关的指令目前存在 bug (dfdx/dfdy/…)
另外目前的运行逻辑是单像素执行,导致微分相关的指令不太好处理,可以说是架构上比较严重的问题,需要改成 4 像素组成 quad 来执行,真正模拟 GPU lanes 相关操作,并且用 SIMD 来加速,进一步的加速则是 JIT/AOT,可能需要利用 LLVM 来做。目前已经着手开始重写了,估计需要比较多的时间,加油吧~
除了 SPVM 虚拟机本身,项目里还实现了一个ShaderToy 模拟器,即支持用 SPVM 来执行 ShaderToy 里的 Shader 效果:

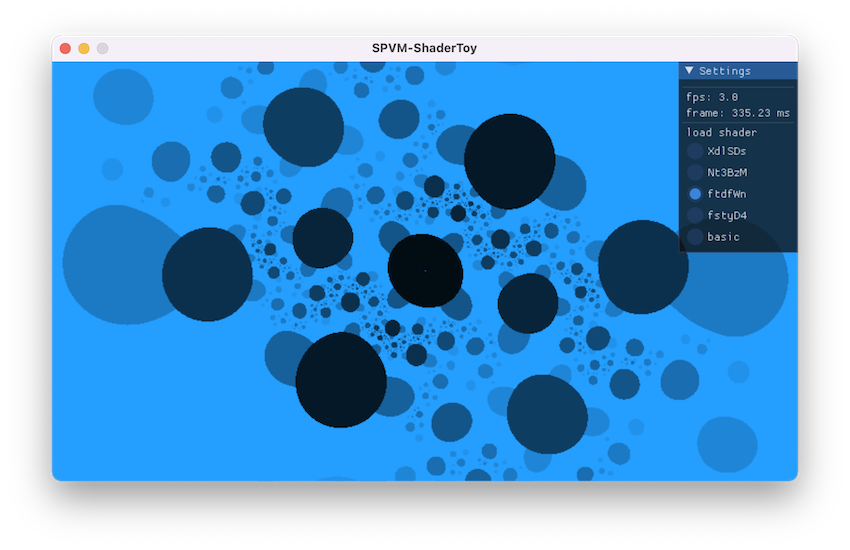
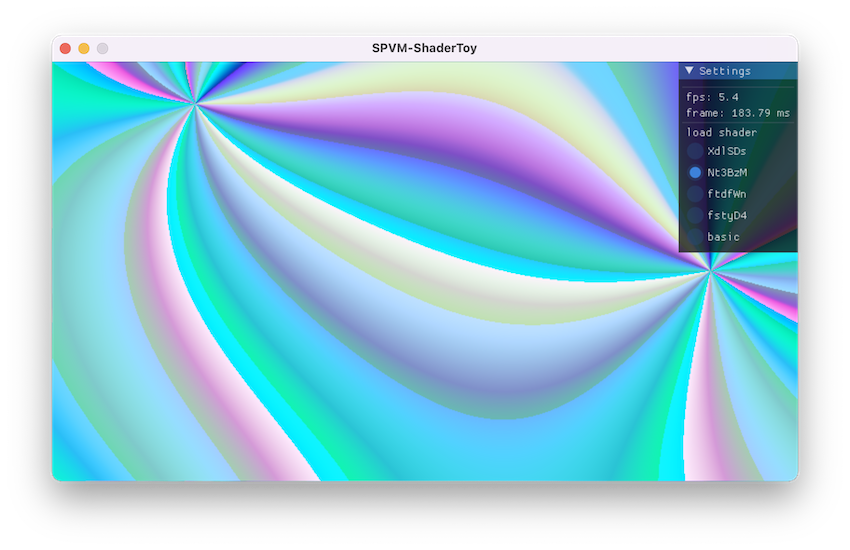
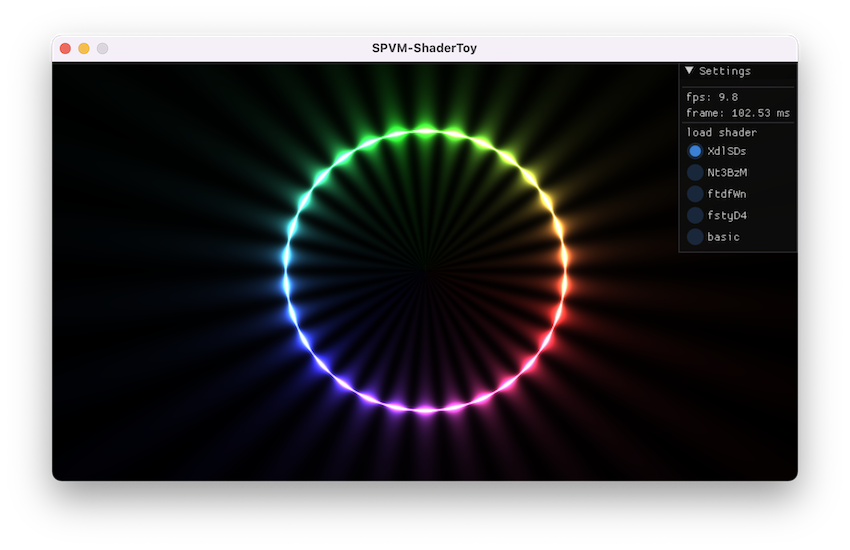
虽然目前帧率奇低,能跑起来还是很开心的~
最后看下 SPVM 的使用示例代码:
GLSL 代码:
#version 450
layout (location = 0) in vec3 inColor;
layout (location = 0) out vec4 outFragColor;
void main()
{
outFragColor = vec4(inColor.yxz, 1.0f);
}使用 SPVM 执行:
#define HEAP_SIZE 128 * 1024
const char *SPV_PATH = "shaders/simple.frag.spv";
SPVM::SpvmModule module;
SPVM::Runtime runtime;
// decode spir-v file
bool success = SPVM::Decoder::decodeFile(SPV_PATH, &module);
if (!success) {
std::cout << "error decode spir-v file";
return -1;
}
// init runtime
success = runtime.initWithModule(&module, HEAP_SIZE);
if (!success) {
std::cout << "error init module";
return -1;
}
// get uniform locations
SPVM::SpvmWord inColorLoc = runtime.getLocationByName("inColor");
SPVM::SpvmWord outFragColorLoc = runtime.getLocationByName("outFragColor");
// write input
float inColor[3]{0.2f, 0.3f, 0.4f};
runtime.writeInput(inColor, inColorLoc);
// execute shader entry function 'main'
success = runtime.execEntryPoint();
if (!success) {
std::cout << "error exec entrypoint function";
return -1;
}
// read output
float outFragColor[4];
runtime.readOutput(outFragColor, outFragColorLoc);
std::cout << "outFragColor[0]: " << outFragColor[0] << std::endl;
std::cout << "outFragColor[1]: " << outFragColor[1] << std::endl;
std::cout << "outFragColor[2]: " << outFragColor[2] << std::endl;
std::cout << "outFragColor[3]: " << outFragColor[3] << std::endl;可以看到流程比较简单,不过目前的对外 API 不够完善,GLSL 内置变量的读写需要手动操作,也不支持指令的调试(如逐行、断点等)。